The last five years or so has been an incredible time to be involved in e-learning. We've seen the rise and demise of the Digital Native, the flight and delight of students and academics to Web 2.0 systems, and the attempted murder of the VLE (we now know that reports of its death have been greatly exaggerated). In our work in the Learning Societies Lab we've played our own small part in that dramatic change through the radical overhaul of teaching and learning repositories, the rejection of traditional Learning Objects and the promotion of Open Educational Resources (OER).
The result of that effort is an unassuming piece of software called EdShare, itself an extension to EPrints (one of the world's most successful research repositories). EdShare was
funded by JISC through a number of projects and is used by the University of Southampton for
its own teaching and learning repository, but its also the software behind the
HUMBox, is being used
by the OU, will be the repository for the
BLOODHOUND Supersonic Car project, and is in place or being planned for at least another ten institutions.
But the technology itself is nothing special, it's the ideas and the philosophy behind it that make it work and I thought it was worth explaining why EdShare looks the way it does.
What is a Repository For?
Our key revelation in developing EdShare came several years ago when (after a few false starts) it became obvious that the traditional approach (digitally packaged teaching resources described using Learning Object metadata) was not working for everyday teachers. The overheads were huge, the upload process complex and the benefits to the people required to do the work (teachers and lecturers) unclear. This was 2007 and we asked ourselves how come people were prepared to upload photos and videos to emerging public sites like Flickr and Youtube, but they couldn't be bothered to share their teaching resources. What do those sites offer that teaching and learning repositories don't?

The problem was that we were translating the research repository model to learning resources, and it didn't fit. Research repositories are about archiving things that are at the end of their lifecycle, users like this archiving service - it's valuable to them. They get a safe, permanent, official and above all highly visible home for their precious work. It's a clear gain for a researcher, and means that they will make the effort to upload.
But who wants to archive their teaching resources? Teaching resources are living things that breath with the passing of each academic year, they evolve and can be rough around the edges. Archiving them is the last thing you want to do!
For inspiration we examined those Web 2.0 sites more carefully and asked ourselves the question - what services do they offer?
We came up with three key things, and decided to make these the underpinning services of our new repository. Based on these services we designed a number of extensions to EPrints that transforms it from an archiving repository to a living-breathing learning and sharing system.
Hosting
The first thing we noticed was that all barriers to uploading had to go - and that includes all that complex Learning Object metadata. It's nice to have, but the main service is to give people an online storage space, and to allow them to see their work
in the browser, describing that work is (at best) of secondary importance. That inline browser view simultaneously turns the repository into a social media platform, whilst also negating the major need for most of the metadata - why read about the resource when you can see it right in front of you?
To make this a reality we implemented an inline preview tool that uses a whole bunch of behind the scenes converters to make whatever you upload visible. It manages images, audio, video, pdfs and (crucially) MS Office files like Word and Powerpoint. Seeing is believing, imagine how god-awful YouTube would be if you had to download every video you wanted to see and mess around installing codecs before you could watch it.
Organisation
Secondly we decided that the system should allow people to manage their resources in the way that they see fit - rather than requiring them to package them up in predetermined ways. This means being open about what can be uploaded, but also means giving people mechanisms to organise it once its uploaded.
To enable this we implemented free tagging and collections. Collections allow people to create a list of resources and give them a name and a description. In return they get a decent presentation page and a url that they can circulate or stick on their web page. Tags are in effect a kind of open-ended public collection, but they are also easy and familiar.
Community
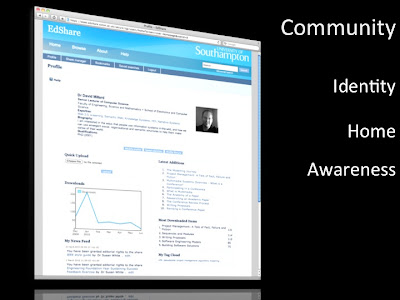
The final service is to help build community by putting the people back into the repository. This doesn't have to be extreme, it doesn't mean reinventing Facebook, instead you can build community through the sharing mechanisms of the repository itself by simply providing a profile page that gathers together all of one person's efforts in the repository, and making sure that uploaders are aware of the activity (the attention metadata) around their items.
We created a profile system (called MePrints) that gathers together all of the information about a user in one place. The profile acts as both a homepage for users and as an identity page for others who get to see who this person is through their activity in the repository. Simple profile widgets such as an event feed show users what activity is happening around their resources, and giving people feedback and encouragement is the best way to keep them engaged.
The EdShare Philosophy
Perhaps the main way to view what we did with EdShare is to see it as an attempt to create a system that actually is valuable to users, rather than the institution. That doesn't mean that the institution doesn't see value - enough to fund the thing for a start - but if users don't benefit then they wont come, no matter how many times you build it.
EPrints Services now offer EdShare as one of their supported packages and the
software itself is available as Open Source, but there are still challenges ahead and EdShare is really just a start. Once we have people adding and sharing content then we need to ensure that others can find it easily, that they can repurpose it, and that the act of repurposing - we call it remixing - is known to the original authors so it reinforces community and leads to further engagement.
We also have to deal with the complex ecology of repositories that is evolving - what is the relationship between the institutional repository and the VLE, what about iTunesU or community repositories? At Southampton we are exploring this by looking at how EdShare sits alongside Blackboard, and by using EdShare as a platform to promote content into iTunesU (so we view EdShare as a working, but transparent, learning content system and ITunesU as a showcase site for the best of the Universities learning material).
So if you are considering creating a teaching and learning repository for your institution then I wish you the best of luck. But remember, sharing is good, but altruism alone wont build your repository. To make it work, you have to make it useful.
You can read more about EdShare in the following pubs:
- Davis, H., Carr, L., Hey, J., Howard, Y., Millard, D., Morris, D. and White, S. (2010) Bootstrapping a Culture of Sharing to Facilitate Open Educational Resources. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 3 (2). pp. 96-109.
- Millard, D. E., Davis, H. C., Howard, Y., McSweeney, P., Francois, S., Morris, D., Ramsden, M. and White, S. (2010) MePrints: Building User Centred Repositories. In: 5th International Conference on Open Repositories, 6-9 July 2010 , Madrid, Spain. (In Press)
- Millard, D. and Howard, Y. (2010) Towards an Ergonomics of Knowledge Systems: Improving the Design of Technology Enhanced Learning. In: European Conference on Technology Enhanced Learning, Sept 28 - Oct 1, 2010, Barcelona (Spain).
- Millard, D., Howard, Y., McSweeney, P., Arrebola, M., Borthwick, K. and Varella, S. (2009) Phantom Tasks and Invisible Rubric: The Challenges of Remixing Learning Objects in the Wild. Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Technology Enhanced Learning . (In Press)
- Millard, D., Howard, Y., McSweeney, P., Borthwick, K., Arrebola, M. and Watson, J. (2009) The Language Box: Re-imagining Teaching and Learning Repositories. In: International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies, July 14-18, 2009, Riga, Latvia.
- Millard, D., Howard, Y., Wills, G., Watson, J. and Arrebola, M. (2008) Towards an Open Repository of Teaching Resources. In: Open Repositories Conference 2008 (OR2008), 1st-4th April 2008, Southampton, United Kingdom